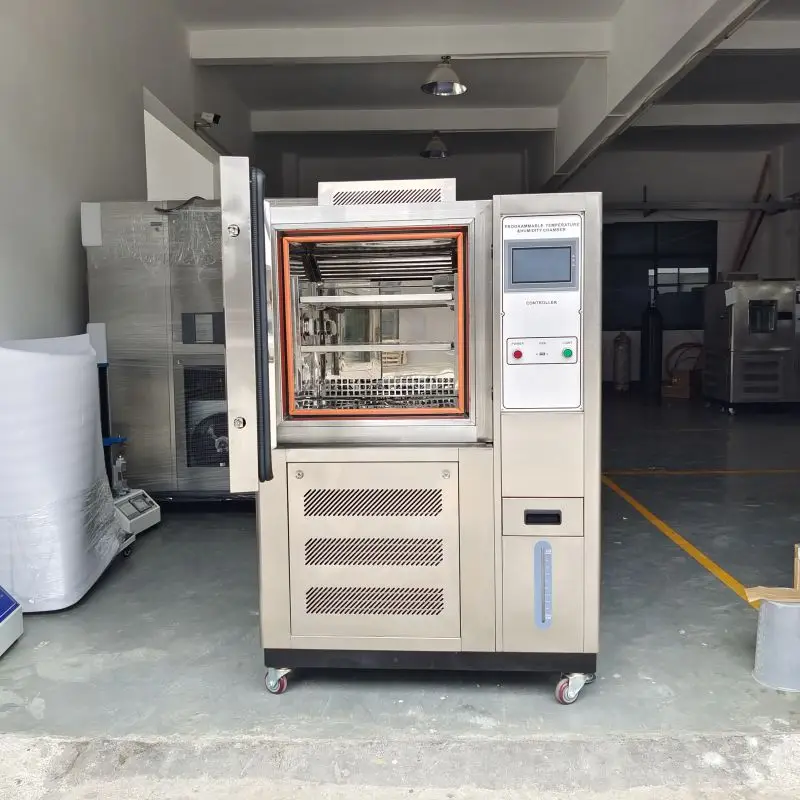
TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY CHAMBER
A Temperature and Humidity Chamber (also known as a Climatic Chamber) is a controlled enclosure designed to test the effects of specific environmental conditions on biological items, industrial products, materials, and electronic components.
In 2026, these chambers are critical for Electric Vehicle (EV) battery testing and semiconductor reliability, ensuring products can survive diverse global climates.
Product Information
1. Core Functions
- Constant Testing: Maintaining a steady temperature and humidity level (e.g., 85°C and 85% relative humidity) for long-duration stability testing.
- Cycling Testing: Programmed to fluctuate between extremes (e.g., from -70°C to +180°C) to simulate day/night cycles or seasonal transitions.
- Accelerated Aging: Forcing a product to “age” by subjecting it to harsh conditions to predict its lifespan and identify potential points of failure.
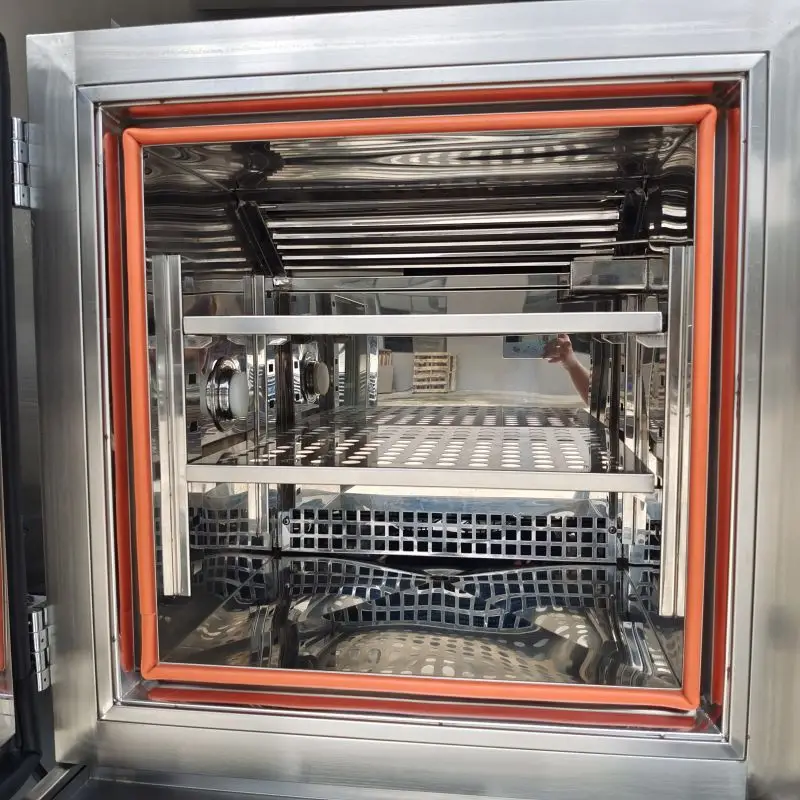
2. How It Works
- Heating/Cooling: Uses electric heaters and mechanical refrigeration (or liquid nitrogen) to reach temperature setpoints.
- Humidity Control: Steam generators or ultrasonic atomizers add moisture, while specialized dehumidification coils or desiccant dryers remove it.
- Airflow: High-velocity fans ensure a uniform environment throughout the entire chamber so that the sample is treated equally on all sides.
3. Key 2026 Technological Features
- Green Refrigerants: Following strict 2026 environmental regulations, most new models utilize low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) refrigerants to reduce their carbon footprint.
- AI Diagnostics: Advanced controllers now feature AI-driven predictive maintenance, notifying users before a sensor or compressor fails to prevent costly test interruptions.
- Remote Cloud Monitoring: Real-time data is synced to mobile apps and cloud platforms, allowing engineers to monitor long-term tests from anywhere in the world.
4. Common Applications
- Electronics: Testing for circuit board corrosion and solder joint fatigue.
- Pharmaceuticals: Mandatory stability studies to determine the shelf life of vaccines and medications.
- Automotive: Evaluating the durability of interior plastics and external sensors against tropical humidity.
- Food & Packaging: Testing how moisture affects packaging integrity and food spoilage.
Be the first to review “TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY CHAMBER”


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.